A type of weather-resistant steel created by alloying copper, chromium, and nickel is corten A. Corten A also contains phosphorus, making it ideal for applications such as gas flues and exterior fascias. The material is not recommended for heavy load-bearing applications.
Corten B is a kind of weather-resistant steel that is best suited for heavy, load-bearing structures.
Speaking of Corten Steel, specialized Corten Steel is used for proper functioning. Cortensteeltube.com Is one leading Manufacturer, Supplier & Stockist Of Corten Steel Grade A Plate & Sheet.
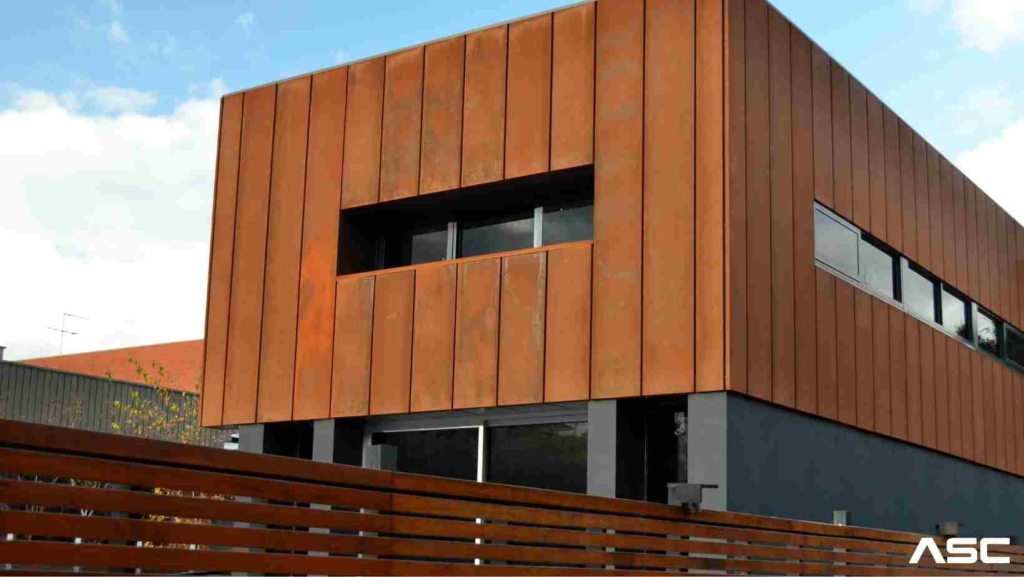

What is Corten Steel
The greatest advantage of Corten A and Corten B is their corrosion resistance. Unlike most low alloy steels on the market, this steel grade does not rust when exposed to moisture.
Corten A and Corten B steels form a corrosion-resistant, protective layer known as a ‘patina’. Rust on this steel is unlike that on standard steel, which does not detach from the surface
Rust is able to penetrate deeper into the metal. Steel beneath the patina is protected, ensuring its strength.
Corten A Weathering Steel
Corten A alloys copper, nickel, and chromium with phosphorus. Corten A’s blend of materials makes it well-suited for gas flue applications. In addition to aesthetic fascias, it is also commonly used for applications that carry heavy loads.
Features
- High durability
- Lightweight
- Corrosion resistance
- Uniform construction
- Strength
- Toughness
Applications
Corten A plate steel is mainly used in container manufacturing, rolling stock, oil rigs, harbor construction, oil platforms, and other structural parts affected by hydrogen sulfide corrosion in petrochemical equipment.
Corten B Weathering Steel
Corten B has a similar composition to Corten A and is used for many structures due to its corrosion resistance. It is, however, much better suited for load-bearing structures than Corten A.
Features
- Higher weather resistance than normal grades
- Minimum yield strength 50 KSI
Application
- Architecture
- Sculpture
- Structural works
- Industrial chimneys
- Freight wagons
- Silos
- Containers
- Pylons
Corten A VS Corten B steel in chemical composition:
| Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Al | V | Cu | Cr | Ni |
| Corten A | 0.12 | 0.25/0.75 | 0.20/0.50 | 0.07/0.15 | 0.030 | 0.015/0.060 | – | 0.25/0.55 | 0.50/1.25 | 0.65 |
| Corten B | 0.16 | 0.30/0. 50 | 0.80/1.25 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 0.020/0.060 | 0.02/0.10 | 0.25/0.40 | 0.40/0.65 | 0.40 |
Corten A VS Corten B steel in mechanical properties:
| Grade | Yield Strength Rel N/mm² Minimum | Tensile Strength Rm N/mm² Minimum | Elongation A50 % Minimum |
| Corten A | 355 | 470-630 | 20 |
| Corten B | 345 | 470-630 | 20 |
Cortensteeltube.com is a leading supplier, stockist, manufacturer & exporter of Corten Steel. Get in touch with us for the best rates & availability Of Corten Steel Grade A Plate & Sheet.
Uses of Corten A and Corten B
COR-TEN steel, also known as Corten A and Corten B, is a type of weathering steel. Although they both have similar properties and are used in various applications, there are some differences between them.
Corten A is a type of weathering steel containing copper, chromium, nickel, and phosphorus. When exposed to the weather, the steel forms a stable rust-like surface that prevents further corrosion. In outdoor sculptures, bridges, and building facades, Corten A is commonly used.
Weathering steel Corten B, on the other hand, contains additional alloys, such as vanadium, copper, and manganese. Additionally, these alloys provide improved corrosion resistance, which is particularly useful in highly saline or acidic environments. Marine applications such as shipping containers and boat hulls commonly use Corten B.
The primary difference between Corten A and Corten B is their chemical composition, with Corten B containing additional alloys that improve corrosion resistance.
Advantages of Corten A and Corten B
Corten A and Corten B are known for forming a stable rust-like surface when exposed to the weather, which provides natural corrosion protection. As a result, Corten steel is a popular choice for outdoor structures and architectural features since it does not require painting or maintenance.
In high-saline or acidic environments, Corten B is more corrosion resistant than Corten A. A marine application, such as a shipping container or a boat hull, benefits from Corten B’s ability to resist corrosion when exposed to saltwater.
Additionally, Corten B’s additional alloys increase strength and durability, making it a popular choice for applications requiring high strength-to-weight ratios, such as bridges and building facades.
In general, the advantages of Corten A and Corten B vary according to the application and environment. Although both types of weathering steel provide natural corrosion protection and eliminate the need for painting and maintenance, Corten B is a better choice for marine and highly corrosive environments.
Corten A and Corten B disadvantages
There are many advantages to Corten A and Corten B, but there are also some disadvantages.
The initial cost of Corten A and Corten B may be a potential disadvantage. Due to its unique properties and the alloys added to improve corrosion resistance, weathering steel can be more expensive than traditional carbon steel. It is possible, however, to offset this cost by reducing the amount of maintenance and painting needed over the steel’s lifetime.
There is also the possibility of staining or runoff. Even though Corten steel is designed to form a stable rust-like surface, some staining or runoff can occur during weathering. In applications where the runoff may damage surrounding materials or structures, this can be a concern.
Furthermore, Corten steel may not be suitable for all applications or aesthetic preferences due to its unique appearance. Some designers may prefer a uniform or traditional look to the rust-like patina, which varies in color and texture.
Corten A and Corten B should be weighed against their advantages based on their specific applications and environments. There are some drawbacks to weathering steel, but it can be a durable and low-maintenance option for a variety of outdoor structures.







Leave A Comment